Color, Reflectance and Transmittance
ElumTools utilizes a multi-purpose dialog to set the Color, Reflectance and Transmittance of any material. Similar dialogs are used to set Transparency and Luminance Color or Spectral Radiant Emittance (SRE). The latter two quantities are not covered in this topic.
A material can have both reflectance and transmittance. However, "Opaque" materials as set in the ElumTools Materials Manager can have only reflectance. If a Transmittance is added to an Opaque material in this dialog, the material will become "Translucent" and this property will then be shown in the "Surface Type" column.
Reflectance and Color
ElumTools calculates the surface reflectance from the Red, Green, and Blue (RGB) components of the material "Graphics Color" in the Revit materials section. This may or may not be the desired color and reflectance for the actual lighting calculation. ElumTools makes it easy to change the color and reflectance as well as store any favorite selections or draw from the most recent twenty colors used.
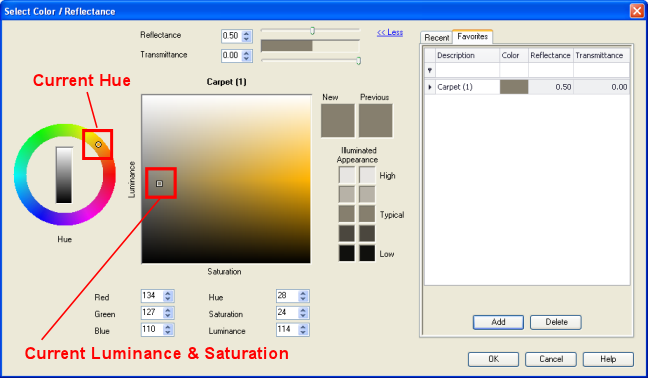
To change a color and its corresponding reflectance, first select a Hue from the circular selection wheel on the left side of the dialog. You can point, click and drag to make your selection. Grayscale selections are in the center of the wheel. Once the Hue is selected, point, click and drag to adjust the Luminance and Saturation for the selected Hue in the center square. Watch the reflectance change for the various selection in the slider at the top of the dialog. You can also move the Reflectance slider to adjust the reflectance for the current Hue, or simply enter a number (decimal) in the cell provided.
It is also very easy to enter colors in terms of RGB or HSL numeric values. This may be the case when attempting to duplicate a paint color.
For reference, the relationship between overall reflectance of a surface and its RGB color equivalent is as follows:
Reflectance = 0.2125 * R + 0.7154 * G + 0.0721 * B
where R,G and B are expressed as numbers between 0 and 1.0 (when RGB is expressed by numbers between 0 and 255, divide by 255).
Transmittance
ElumTools will allow a Transmittance to be assigned to any material. If you have not selected a translucent material in the Materials Manager "Surface Type" selection, but assign a transmittance within the Color and Reflectance dialog, ElumTools will change the surface type to "Translucent" when you exit the Color dialog.
| If a material has a set reflectance, the transmittance is limited and can be easily adjusted using the slider. Where the reflectance and Transmittance sliders meet will be the limiting point for both quantities. Note that this total will not add up to 100% as the remainder of the light is absorbed by the color selected. |
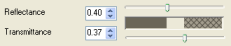
|
Transmittance is limited by the following relationship based on the premise that all light that is not reflected or absorbed can be transmitted. The following equation is applied to the remaining, non-reflected light (available).
Transmittance = (0.2125)(Ravail) + (0.7154)(Gavail) + (0.0721)(Bavail)
To compute the maximum transmittance for any particular color we first must find the percentage of each component (Red, Green, Blue) that is available for transmittance. Fortunately, the dialog performs these calculations for you!
Consider the following example:
Suppose we have a color (somewhat of a subdued red) with the following components, R=210, G=105, B=105. What is the maximum transmittance?
Begin by computing the percentages of each component that can be reflected. What is not reflected or absorbed, is then available to be transmitted. We know that full saturation of any color is 255. Divide each component by 255 to find the maximum amount that can be reflected.
Max reflected R = 210/255 = 0.824
Max reflected G = 105/255 = 0.412
Max reflected B = 105/255 = 0.412
To find the maximum amount of light that can be transmitted we must look at which component of the color allows the most light to be reflected, as this color then has the least amount of available light remaining to transmit. In non-dichroic transmittance, the other colors must follow in proportion. In our example, the Red (R) component has the greatest reflected component (that's why it looks red). The maximum transmitted amount of red is then whatever is remaining after reflection.
Max transmitted R = 1 - 0.824 = 0.176
The ratio of transmitted to reflected light for red is 0.176/0.824 = 0.2135
Apply this multiplier to the other color components to arrive at the relative amounts of light that can be transmitted:
Green: 0.2135 x 0.412 = 0.088
Blue: 0.2135 x 0.412 = 0.088
Note that Red also has the greatest transmitted component, so the light that passes through will be reddish in appearance.
Now plug these relative amounts of transmissible light into the equation for Transmittance:
Transmittance = (0.2125)(0.176) + (0.7154)(0.088) + (0.0721)(0.088) = 0.1004
The maximum transmittance for our example color is then 0.1004, or roughly ten percent. (As a side note, since 50% of the light striking this surface was reflected and 10% was transmitted, that leaves 40% to be absorbed.)
Recent Tab
The Recent tab will store the twenty most recently used selections. Each selection can have all three properties: color, reflectance and transmittance. A selection is stored each time the you exit the dialog by selecting the OK button. Once a total of twenty selections has been reached, the oldest selection will drop from the list. If you like a specific selection, be sure to use the Favorites tab.
Favorites Tab
The Color and Reflectance dialog will store an unlimited number of your favorite selections for use with other materials or in other projects. With the color, reflectance and transmittance selection set in the dialog, click on the Favorites tab followed by the Add button. To retrieve it simply click anywhere on the selection in the Favorites tab. Favorites can be sorted by clicking on the column headings if desired, by reflectance for example. Delete your unwanted favorites using the Delete key.
